Sasmirala Individual Information for NGC 1275
Description
NGC 1275 is an infrared-luminous, radio-loud peculiar giant elliptical galaxy at a redshift of z = 0.0175 (D ~ 72.7 Mpc) with a FR I radio morphology and prominent galactic-scale gas filaments. This well-studied object is the central galaxy in the Perseus cluster and one of the original six Seyfert galaxies ([seyfert_nuclear_1943]; see [scharwachter_kinematics_2013] for a recent detailed study). It is presumably in a post-merger state [holtzman_planetary_1992, conselice_nature_2001] and features complex optical spectral properties, leading to many different classifications like Sy 2, borderline Sy 1.5/LINER, BL Lac and even Sy/H II composite [khachikian_atlas_1974, ho_search_1997, veron_ngc1275_1978, veron_agns_1997]. The nucleus is a compact source with a flat spectrum at radio wavelengths, and a pair of galactic-scale jets emerge from it with a PA~ 160∘ in the central kiloparsec region [pedlar_radio_1990, walker_detection_1994, vermeulen_discovery_1994]. Pioneering MIR observations of NGC 1275 were performed by [low_proceedings_1968] and [kleinmann_observations_1970], followed by [rieke_variability_1972, rieke_infrared_1978], [lebofsky_extinction_1979], [aitken_question_1981], [malkan_stellar_1983], [gear_thermal_1985], and [roche_atlas_1991]. The first subarcsecond-resolution N-band image obtained with Keck/LWS show an unresolved nucleus without any extended emission [soifer_high_2003]. NGC 1275 was also observed with ISO [rigopoulou_large_1999, tran_isocam-cvf_2001, siebenmorgen_isocam_2004, temi_cold_2004] and Spitzer/IRAC, IRS and MIPS in the MIR. The corresponding IRAC and MIPS images are dominated by a bright compact nucleus. The IRS LR staring-mode spectrum exhibits silicate 10 and 18 μm emission, a very weak PAH 11.3 μm features and a steep red spectral slope in νFν-space (see also [weedman_mid-infrared_2005, shi_aromatic_2007, leipski_spitzer_2009, mullaney_defining_2011]). Thus, the arcsecond-scale MIR SED verifies the existence of large amounts of AGN-heated dust in NGC 1275, while any star-formation contribution is at least minor [leipski_spitzer_2009]. NGC 1275 was observed with Michelle in the Si-2 and Si-6 filters in 2006 and with COMICS in the N11.7 and NEII filters in 2009 (unpublished, to our knowledge). A bright compact nucleus without further host emission was detected in all images. It appears to be marginally resolved in the sharpest image (Si-2) but displays inconsistent nuclear shapes between the Michelle and COMICS images. Therefore, its MIR extension at subarcsecond resolution remains uncertain. Our nuclear photometry is generally consistent with the Spitzer spectrophotometry with the Michelle fluxes being systematically lower and the COMICS flux systematically higher. We use the IRS spectrum to compute the nuclear 12 μm continuum emission estimate corrected for the silicate feature. Comparison with the historical N-band photometry shows apparent flux variations on the order of ~ 16% during the last ~ 40 years. This indicates intrinsic variability in the N-band emission of NGC 1275 despite uncertainties and systematics of the different instruments, filters and measurement methods.
- [aitken_question_1981] D. K. Aitken, P. F. Roche, and M. M. Phillips. The question of extinction in active galactic nuclei - infrared spectral observations of NGC 1614, NGC 7469 and NGC 1275 . MNRAS , 196 pp. 101P–107P, September 1981.
- [conselice_nature_2001] Christopher J. Conselice, John S. Gallagher, and Rosemary F. G. Wyse. On the nature of the NGC 1275 system . AJ , 122 pp. 2281–2300, November 2001.
- [gear_thermal_1985] W. K. Gear, E. I. Robson, G. Gee, and I. G. Nolt. Thermal and non-thermal emission from NGC 1275 (3C 84) . MNRAS , 217 pp. 281–290, November 1985.
- [ho_search_1997] Luis C. Ho, Alexei V. Filippenko, Wallace L. W. Sargent, and Chien Y. Peng. A search for ``Dwarf'' seyfert nuclei. IV. nuclei with broad h alpha emission . ApJS , 112 pp. 391, October 1997.
- [holtzman_planetary_1992] J. A. Holtzman, S. M. Faber, E. J. Shaya, T. R. Lauer, J. Groth, D. A. Hunter, W. A. Baum, S. P. Ewald, J. J. Hester, R. M. Light, C. R. Lynds, E. J. O'Neil, and J. A. Westphal. Planetary camera observations of NGC 1275 - discovery of a central population of compact massive blue star clusters . AJ , 103 pp. 691–702, March 1992.
- [khachikian_atlas_1974] E. Y. Khachikian and D. W. Weedman. An atlas of seyfert galaxies . ApJ , 192 pp. 581–589, September 1974.
- [kleinmann_observations_1970] D. E. Kleinmann and F. J. Low. Observations of infrared galaxies . ApJL , 159 pp. L165, March 1970.
- [lebofsky_extinction_1979] M. J. Lebofsky and G. H. Rieke. Extinction in infrared-emitting galactic nuclei . ApJ , 229 pp. 111–117, April 1979.
- [leipski_spitzer_2009] C. Leipski, R. Antonucci, P. Ogle, and D. Whysong. The spitzer view of FR i radio galaxies: On the origin of the nuclear mid-infrared continuum . ApJ , 701 pp. 891–914, August 2009.
- [low_proceedings_1968] J. Low and D. E. Kleinmann. Proceedings of the conference on seyfert galaxies and related objects: 17. infrared observations of seyfert galaxies, quasistellar sources, and planetary nebulae . AJ , 73 pp. 868, November 1968.
- [malkan_stellar_1983] M. A. Malkan and A. V. Filippenko. The stellar and nonstellar continua of seyfert galaxies nonthermal emission in the near-infrared . ApJ , 275 pp. 477–492, December 1983.
- [mullaney_defining_2011] J. R. Mullaney, D. M. Alexander, A. D. Goulding, and R. C. Hickox. Defining the intrinsic AGN infrared spectral energy distribution and measuring its contribution to the infrared output of composite galaxies . MNRAS , page 474, April 2011.
- [pedlar_radio_1990] A. Pedlar, H. S. Ghataure, R. D. Davies, B. A. Harrison, R. Perley, P. C. Crane, and S. W. Unger. The radio structure of NGC1275 . MNRAS , 246 pp. 477, October 1990.
- [rieke_infrared_1978] G. H. Rieke. The infrared emission of seyfert galaxies . ApJ , 226 pp. 550–558, December 1978.
- [rieke_variability_1972] G. H. Rieke and F. J. Low. Variability of extragalactic sources at 10 microns . ApJL , 177 pp. L115, November 1972.
- [rigopoulou_large_1999] D. Rigopoulou, H. W. W. Spoon, R. Genzel, D. Lutz, A. F. M. Moorwood, and Q. D. Tran. A large mid-infrared spectroscopic and near-infrared imaging survey of ultraluminous infrared galaxies: Their nature and evolution . AJ , 118 pp. 2625–2645, December 1999.
- [roche_atlas_1991] Patrick F. Roche, David K. Aitken, Craig H. Smith, and Martin J. Ward. An atlas of mid-infrared spectra of galaxy nuclei . MNRAS , 248 pp. 606–629, February 1991.
- [scharwachter_kinematics_2013] J. Scharwächter, P. J. McGregor, M. A. Dopita, and T. L. Beck. Kinematics and excitation of the molecular hydrogen accretion disc in NGC 1275 . MNRAS , 429 pp. 2315–2332, March 2013.
- [seyfert_nuclear_1943] Carl K. Seyfert. Nuclear emission in spiral nebulae. . ApJ , 97 pp. 28, January 1943.
- [shi_aromatic_2007] Yong Shi, Patrick Ogle, George H. Rieke, Robert Antonucci, Dean C. Hines, Paul S. Smith, Frank J. Low, Jeroen Bouwman, and Christopher Willmer. Aromatic features in AGNs: star-forming infrared luminosity function of AGN host galaxies . ApJ , 669 pp. 841–861, November 2007.
- [siebenmorgen_isocam_2004] R. Siebenmorgen, W. Freudling, E. Krügel, and M. Haas. ISOCAM survey and dust models of 3CR radio galaxies and quasars . A&A , 421 pp. 129–145, July 2004.
- [soifer_high_2003] B. T. Soifer, J. J. Bock, K. Marsh, G. Neugebauer, K. Matthews, E. Egami, and L. Armus. High spatial resolution mid-infrared observations of three seyfert galaxies . AJ , 126 pp. 143–152, July 2003.
- [temi_cold_2004] Pasquale Temi, Fabrizio Brighenti, William G. Mathews, and Jesse D. Bregman. Cold dust in early-type galaxies. i. observations . ApJS , 151 pp. 237–269, April 2004.
- [tran_isocam-cvf_2001] Q. D. Tran, D. Lutz, R. Genzel, D. Rigopoulou, H. W. W. Spoon, E. Sturm, M. Gerin, D. C. Hines, A. F. M. Moorwood, D. B. Sanders, N. Scoville, Y. Taniguchi, and M. Ward. Isocam-cvf 5-12 micron spectroscopy of ultraluminous infrared galaxies . ApJ , 552 pp. 527–543, May 2001.
- [vermeulen_discovery_1994] R. C. Vermeulen, A. C. S. Readhead, and D. C. Backer. Discovery of a nuclear counterjet in NGC 1275: A new way to probe the parsec-scale environment . ApJL , 430 pp. L41–L44, July 1994.
- [veron_agns_1997] P. Veron, A. C. Goncalves, and M.-P. Veron-Cetty. AGNs with composite spectra. . A&A , 319 pp. 52–66, March 1997.
- [veron_ngc1275_1978] P. Veron. NGC1275 - a BL lacertae object . Nature , 272 pp. 430, March 1978.
- [walker_detection_1994] R. C. Walker, J. D. Romney, and J. M. Benson. Detection of a VLBI counterjet in NGC 1275: A possible probe of the parsec-scale accretion region . ApJL , 430 pp. L45–L48, July 1994.
- [weedman_mid-infrared_2005] D. W. Weedman, Lei Hao, S. J. U. Higdon, D. Devost, Yanling Wu, V. Charmandaris, B. Brandl, E. Bass, and J. R. Houck. Mid-infrared spectra of classical AGNs observed with the spitzer space telescope . ApJ , 633 pp. 706–716, November 2005.
Images
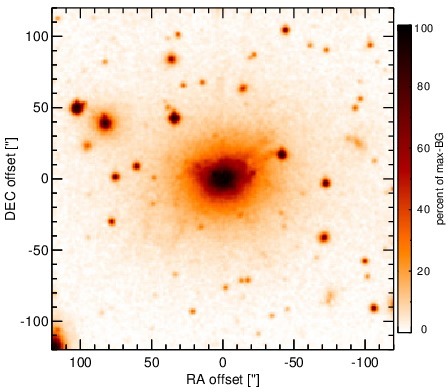
Optical image (DSS, red filter). Displayed are the central 4 arcmin with North being up and East to the left. The colour scaling is linear with white corresponding to the median background (BG) and black to the 0.01% pixels with the highest intensity.
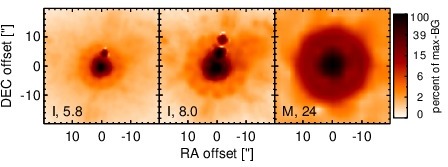
Spitzer MIR images. Displayed are the inner 40 arcsec with North being up and East to the left. The colour scaling is logarithmic with white corresponding to median BG and black to the 0.1% pixels with the highest intensity. The label in the bottom left states instrument and central wavelength of the filter in micron (I: IRAC, M: MIPS).
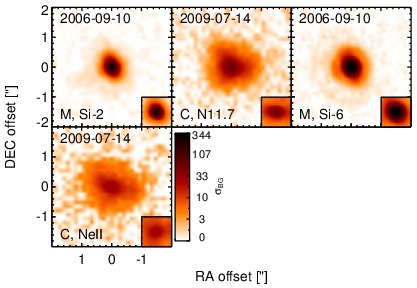
Subarcsecond-resolution MIR images sorted by increasing filter central wavelength. Displayed are the inner 4 arcsec with North being up and East to the left. The colour scaling is logarithmic with white corresponding to median BG and black to the 75% of the highest intensity of all images in units of sig_bg. The inset image (where present; either bottom or top right) shows the central arcsecond of the PSF from the calibrator star, scaled to match the science target. The labels in the bottom left state instrument and filter names (C: COMICS, M: Michelle, T: T-ReCS, V: VISIR).
SEDs
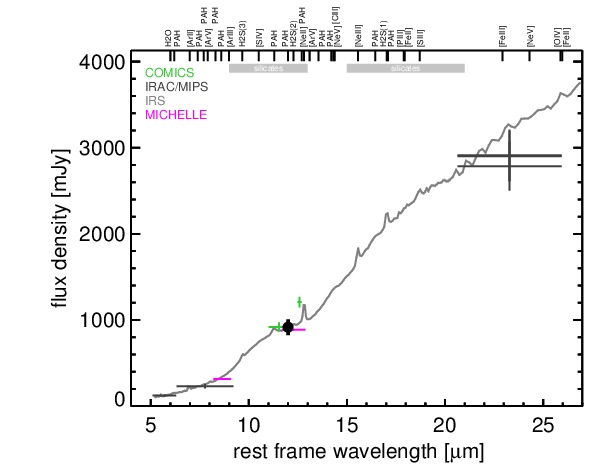
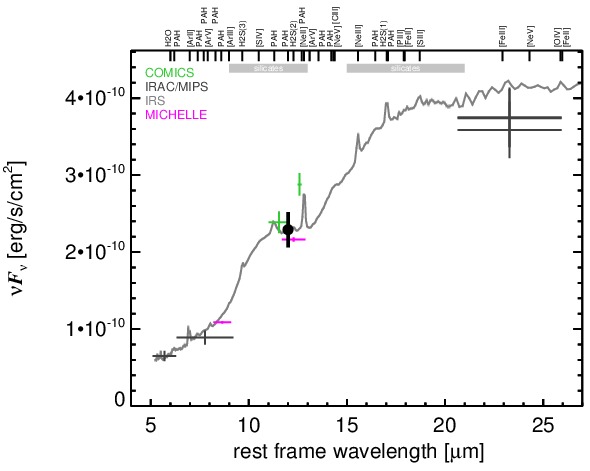
MIR SED. The description of the symbols in all the SED plots (where present) is the following: Grey crosses and solid lines mark the Spitzer/IRAC, MIPS and IRS data. The colour coding of the other symbols is as follows: green for COMICS, magenta for Michelle, blue for T-ReCS and red for VISIR data. Darker-coloured solid lines mark spectra of the corresponding instrument. The black filled circles mark the nuclear 12 and 18 micron continuum emission estimate from the data (where present). The ticks on the top axis mark positions of common MIR emission lines, while the light grey horizontal bars mark wavelength ranges affected by the silicate 10 and 18 micron features.