Sasmirala Individual Information for NGC 4507
Description
NGC 4507 is a face-on barred spiral galaxy at a redshift of z = 0.0118 (D ~ 57.5 Mpc) that hosts a Sy 2 nucleus [kewley_optical_2001] with polarized broad emission lines [moran_frequency_2000]. The AGN is one of the X-ray flux-brightest type II objects, belongs to the nine-month BAT AGN sample, and is also variable in X-rays. Subarcsecond-resolution radio observations reveal a slightly elongated nucleus along a PA~ 10∘ [morganti_radio_1999]. The NLR appears one-sided in [O III] along a PA~-35∘ with an extent of ~ 2arcsec ~ 0.5 kpc [schmitt_hubble_2003]. The first ground-based MIR observations were performed by [glass_mid-infrared_1982], followed by ISO observations [clavel_2.5-11_2000, ramos_almeida_mid-infrared_2007]. The Spitzer/IRAC and MIPS images are dominated by the bright nucleus embedded within the much weaker spiral-like host emission. Note that the IRAC 8.0 μm PBCD image is saturated and, thus, not analysed. Surprisingly, the Spitzer/IRS LR staring-mode spectrum exhibits weak silicate 10 μm and possible 18 μm emission more reminiscent for an unobscured AGN. In addition, only weak PAH features are present and the continuum peaks at ~ 18 μm in νFν-space (see also [shi_9.7_2006, mullaney_defining_2011]). Thus, the arcsecond-scale MIR emission of NGC 4507 is dominated by the AGN without any significant contribution from star formation. We observed the nuclear region of NGC 4507 with VISIR in three narrow N-band filters in 2006 [horst_mid_2008, horst_mid-infrared_2009] and obtained a LR N-band spectrum in 2008 [honig_dusty_2010-1]. In all images, an unresolved nucleus without any host emission was detected. The remeasured nuclear fluxes agree with [horst_mid_2008], the VISIR spectrum and the Spitzer spectrophotometry. Note that the VISIR spectrum does not exhibit any PAH emission, which verifies that the nuclear MIR SED is not star-formation contaminated. The nuclear MIR emission of NGC 4507 has been resolved with MIDI interferometric observations and was modelled as two components with sizes of ~ 4 and ~ 12 pc [burtscher_diversity_2013].
- [burtscher_diversity_2013] L. Burtscher, K. Meisenheimer, K. R. W. Tristram, W. Jaffe, S. F. Hönig, R. I. Davies, M. Kishimoto, J.-U. Pott, H. Röttgering, M. Schartmann, G. Weigelt, and S. Wolf. A diversity of dusty AGN tori. data release for the VLTI/MIDI AGN large program and first results for 23 galaxies . A&A , 558 pp. 149, October 2013.
- [clavel_2.5-11_2000] J. Clavel, B. Schulz, B. Altieri, P. Barr, P. Claes, A. Heras, K. Leech, L. Metcalfe, and A. Salama. 2.5-11 micron spectroscopy and imaging of AGNs. implication for unification schemes . A&A , 357 pp. 839–849, May 2000.
- [glass_mid-infrared_1982] I. S. Glass, A. F. M. Moorwood, and W. Eichendorf. Mid-infrared observations of seyfert 1 and narrow-line x-ray galaxies . A&A , 107 pp. 276–282, March 1982.
- [honig_dusty_2010-1] S. F. Hönig, M. Kishimoto, P. Gandhi, A. Smette, D. Asmus, W. Duschl, M. Polletta, and G. Weigelt. The dusty heart of nearby active galaxies. i. high-spatial resolution mid-IR spectro-photometry of seyfert galaxies . A&A , 515 pp. 23, June 2010.
- [horst_mid-infrared_2009] H. Horst, W. J. Duschl, P. Gandhi, and A. Smette. Mid-infrared imaging of 25 local AGN with VLT-VISIR . A&A , 495 pp. 137–146, February 2009.
- [horst_mid_2008] H. Horst, P. Gandhi, A. Smette, and W. J. Duschl. The mid IR - hard x-ray correlation in AGN and its implications for dusty torus models . A&A , 479 pp. 389–396, February 2008.
- [kewley_optical_2001] L. J. Kewley, C. A. Heisler, M. A. Dopita, and S. Lumsden. Optical classification of southern warm infrared galaxies . ApJS , 132 pp. 37–71, January 2001.
- [moran_frequency_2000] Edward C. Moran, Aaron J. Barth, Laura E. Kay, and Alexei V. Filippenko. The frequency of polarized broad emission lines in type 2 seyfert galaxies . ApJL , 540 pp. L73–L77, September 2000.
- [morganti_radio_1999] R. Morganti, Z. I. Tsvetanov, J. Gallimore, and M. G. Allen. Radio continuum morphology of southern seyfert galaxies . A&AS , 137 pp. 457–471, June 1999.
- [mullaney_defining_2011] J. R. Mullaney, D. M. Alexander, A. D. Goulding, and R. C. Hickox. Defining the intrinsic AGN infrared spectral energy distribution and measuring its contribution to the infrared output of composite galaxies . MNRAS , page 474, April 2011.
- [ramos_almeida_mid-infrared_2007] C. Ramos Almeida, A. M. Pérez García, J. A. Acosta-Pulido, and J. M. Rodríguez Espinosa. The mid-infrared emission of seyfert galaxies: A new analysis of ISOCAM data . AJ , 134 pp. 2006–2019, November 2007.
- [schmitt_hubble_2003] H. R. Schmitt, J. L. Donley, R. R. J. Antonucci, J. B. Hutchings, and A. L. Kinney. A hubble space telescope survey of extended [o III] λ5007 emission in a far-infrared selected sample of seyfert galaxies: Observations . ApJS , 148 pp. 327–352, October 2003.
- [shi_9.7_2006] Y. Shi, G. H. Rieke, D. C. Hines, V. Gorjian, M. W. Werner, K. Cleary, F. J. Low, P. S. Smith, and J. Bouwman. 9.7 μm silicate features in active galactic nuclei: New insights into unification models . ApJ , 653 pp. 127–136, December 2006.
Images
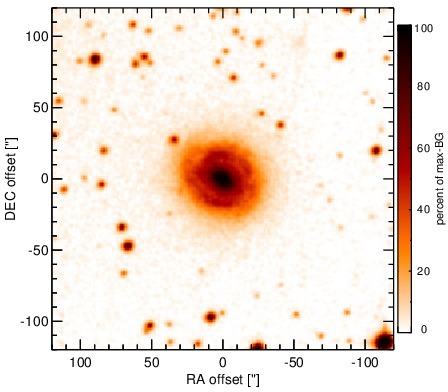
Optical image (DSS, red filter). Displayed are the central 4 arcmin with North being up and East to the left. The colour scaling is linear with white corresponding to the median background (BG) and black to the 0.01% pixels with the highest intensity.
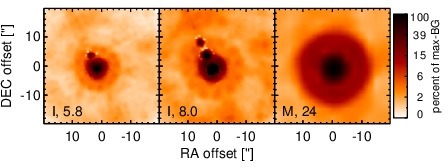
Spitzer MIR images. Displayed are the inner 40 arcsec with North being up and East to the left. The colour scaling is logarithmic with white corresponding to median BG and black to the 0.1% pixels with the highest intensity. The label in the bottom left states instrument and central wavelength of the filter in micron (I: IRAC, M: MIPS).
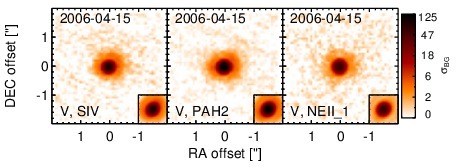
Subarcsecond-resolution MIR images sorted by increasing filter central wavelength. Displayed are the inner 4 arcsec with North being up and East to the left. The colour scaling is logarithmic with white corresponding to median BG and black to the 75% of the highest intensity of all images in units of sig_bg. The inset image (where present; either bottom or top right) shows the central arcsecond of the PSF from the calibrator star, scaled to match the science target. The labels in the bottom left state instrument and filter names (C: COMICS, M: Michelle, T: T-ReCS, V: VISIR).
SEDs
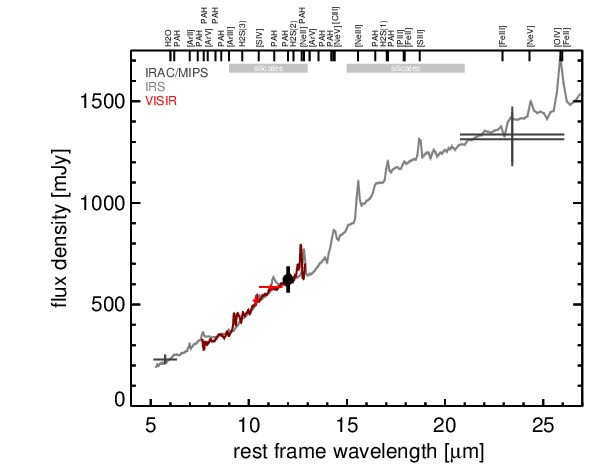
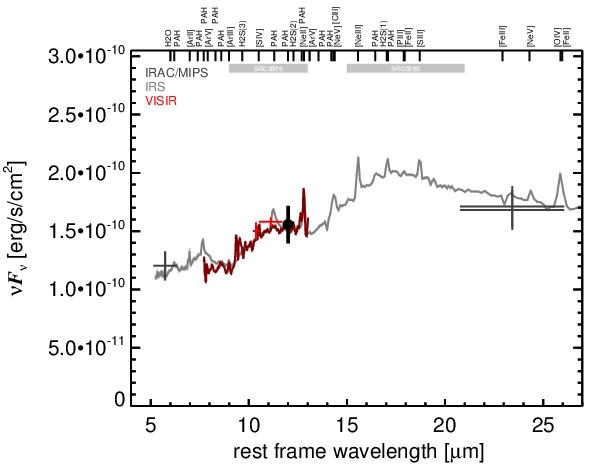
MIR SED. The description of the symbols in all the SED plots (where present) is the following: Grey crosses and solid lines mark the Spitzer/IRAC, MIPS and IRS data. The colour coding of the other symbols is as follows: green for COMICS, magenta for Michelle, blue for T-ReCS and red for VISIR data. Darker-coloured solid lines mark spectra of the corresponding instrument. The black filled circles mark the nuclear 12 and 18 micron continuum emission estimate from the data (where present). The ticks on the top axis mark positions of common MIR emission lines, while the light grey horizontal bars mark wavelength ranges affected by the silicate 10 and 18 micron features.