Sasmirala Individual Information for NGC 5135
Description
NGC 5135 is an infrared-luminous face-on barred spiral galaxy at a redshift of z = 0.0137 (D ~ Mpc). It harbours a Sy 2 nucleus [veron-cetty_catalogue_2010] and a circum-nuclear starburst [gonzalez_delgado_ultraviolet-optical_1998, bedregal_near-ir_2009]. The latter has a knotty morphology and extends over ~ 3arcsec ~ 0.9 kpc. A compact radio source with faint extended emission up to ~ 9arcsec ~ 2.8 kpc to the north-east (PA~ 30∘) was detected at lower resolution [ulvestad_radio_1989] and is presumably associated with a compact star-forming region ~ 3arcsec ~ 0.3 kpc south of the nucleus and not with the AGN [levenson_accretion_2004]. This agrees with the non-detection in subarcsecond-resolution radio observations [thean_high-resolution_2000]. The [O III] emission is extended in north-south direction on a scale of ~ 2arcsec ~ pc [gonzalez_delgado_ultraviolet-optical_1998]. The first ground-based MIR observations of NGC 5135 were performed by [wynn-williams_luminous_1993], followed by [maiolino_new_1995] and [gorjian_10_2004], the latter authors reporting the first subarcsecond-resolution N-band photometry. The Spitzer/IRAC and MIPS images show an extended nucleus embedded within the spiral-like host emission. The IRAC 8.0 μm PBCD image is saturated in the nucleus and, thus, not analysed (but see [gallimore_infrared_2010]). Our nuclear IRAC 5.8 μm flux is consistent with [alonso-herrero_high_2006] and [u_spectral_2012] but not [gallimore_infrared_2010]. The Spitzer/IRS LR staring-mode spectrum is dominated by PAH emission with prominent silicate 10 μm absorption and a red spectral slope in νFν-space (see also [shi_9.7_2006, wu_spitzer/irs_2009, tommasin_spitzer-irs_2010, gallimore_infrared_2010, alonso-herrero_local_2012]). Thus, the arcsecond-scale MIR SED is star-formation dominated. The nuclear region of NGC 5135 was observed with T-ReCS in the broad N filter in 2006 [alonso-herrero_high_2006], and with VISIR in five different narrow N-band filters in 2006 and 2008 (partly published in [horst_mid_2008, horst_mid-infrared_2009]). In addition, a T-ReCS LR N-band spectrum was obtained by [diaz-santos_high_2010]. In all cases, a compact nucleus partly surrounded by banana-shaped, clumpy extended emission was detected. The inner radius of this emission is located at ~ 1arcsec ~ 300 pc from the nucleus, and the outer radius is located at ~ 2.5arcsec ~ 750 pc from the nucleus, extending from PA~ 65∘ to PA~ 214∘. The nucleus itself is unresolved in the sharpest images (NEII_1 and NEII from 2006). Therefore, we assume that the apparent extensions found in several images are non-intrinsic and the nucleus of NGC 5135 is generally unresolved at subarcsecond resolution in the MIR. Our nuclear photometry is consistent with the values published by [horst_mid_2008] and the T-ReCS spectrum as published by [gonzalez-martin_dust_2013], while being on average ~ 72% lower than the Spitzer spectrophotometry. The nuclear MIR SED exhibits deep silicate absorption but no PAH features, which indicates that the AGN-powered emission has been isolated. However, star-formation dominates the MIR emission of the central ~ 1 kpc of NGC 5135.
- [alonso-herrero_high_2006] Almudena Alonso-Herrero, Luis Colina, Christopher Packham, Tanio Díaz-Santos, George H. Rieke, James T. Radomski, and Charles M. Telesco. High spatial resolution t-ReCS mid-infrared imaging of luminous infrared galaxies . ApJ , 652 pp. L83–L87, December 2006.
- [alonso-herrero_local_2012] Almudena Alonso-Herrero, Miguel Pereira-Santaella, George H. Rieke, and Dimitra Rigopoulou. Local luminous infrared galaxies. II. active galactic nucleus activity from Spitzer/Infrared spectrograph spectra . ApJ , 744 pp. 2, January 2012.
- [bedregal_near-ir_2009] Alejandro G. Bedregal, Luis Colina, Almudena Alonso-Herrero, and Santiago Arribas. Near-IR integral field spectroscopy study of the star formation and AGN of the LIRG NGC 5135 . ApJ , 698 pp. 1852–1871, June 2009.
- [diaz-santos_high_2010] Tanio Díaz-Santos, Almudena Alonso-Herrero, Luis Colina, Christopher Packham, N. A. Levenson, Miguel Pereira-Santaella, Patrick F. Roche, and Charles M. Telesco. A high spatial resolution mid-infrared spectroscopic study of the nuclei and star-forming regions in luminous infrared galaxies . ApJ , 711 pp. 328–349, March 2010.
- [gallimore_infrared_2010] J. F. Gallimore, A. Yzaguirre, J. Jakoboski, M. J. Stevenosky, D. J. Axon, S. A. Baum, C. L. Buchanan, M. Elitzur, M. Elvis, C. P. O'Dea, and A. Robinson. Infrared spectral energy distributions of seyfert galaxies: Spitzer space telescope observations of the 12 μm sample of active galaxies . ApJS , 187 pp. 172–211, March 2010.
- [gonzalez-martin_dust_2013] O. González-Martín, J. M. Rodríguez-Espinosa, T. Díaz-Santos, C. Packham, A. Alonso-Herrero, P. Esquej, C. Ramos Almeida, R. Mason, and C. Telesco. Dust in active galactic nuclei. mid-infrared t-ReCS/Gemini spectra using the new RedCan pipeline . A&A , 553 pp. 35, May 2013.
- [gonzalez_delgado_ultraviolet-optical_1998] Rosa M. González Delgado, Timothy Heckman, Claus Leitherer, Gerhardt Meurer, Julian Krolik, Andrew S. Wilson, Anne Kinney, and Anuradha Koratkar. Ultraviolet-optical observations of the seyfert 2 galaxies NGC 7130, NGC 5135, and IC 3639: Implications for the starburst-active galactic nucleus connection . ApJ , 505 pp. 174–198, September 1998.
- [gorjian_10_2004] V. Gorjian, M. W. Werner, T. H. Jarrett, D. M. Cole, and M. E. Ressler. 10 micron imaging of seyfert galaxies from the 12 micron sample . ApJ , 605 pp. 156–167, April 2004.
- [horst_mid-infrared_2009] H. Horst, W. J. Duschl, P. Gandhi, and A. Smette. Mid-infrared imaging of 25 local AGN with VLT-VISIR . A&A , 495 pp. 137–146, February 2009.
- [horst_mid_2008] H. Horst, P. Gandhi, A. Smette, and W. J. Duschl. The mid IR - hard x-ray correlation in AGN and its implications for dusty torus models . A&A , 479 pp. 389–396, February 2008.
- [levenson_accretion_2004] N. A. Levenson, K. A. Weaver, T. M. Heckman, H. Awaki, and Y. Terashima. Accretion and outflow in the active galactic nucleus and starburst of NGC 5135 . ApJ , 602 pp. 135–147, February 2004.
- [maiolino_new_1995] R. Maiolino, M. Ruiz, G. H. Rieke, and L. D. Keller. New constraints on the unified model of seyfert galaxies . ApJ , 446 pp. 561, June 1995.
- [shi_9.7_2006] Y. Shi, G. H. Rieke, D. C. Hines, V. Gorjian, M. W. Werner, K. Cleary, F. J. Low, P. S. Smith, and J. Bouwman. 9.7 μm silicate features in active galactic nuclei: New insights into unification models . ApJ , 653 pp. 127–136, December 2006.
- [thean_high-resolution_2000] Andy Thean, Alan Pedlar, Marek J. Kukula, Stefi A. Baum, and Christopher P. O'Dea. High-resolution radio observations of seyfert galaxies in the extended 12-μm sample - i. the observations . MNRAS , 314 pp. 573–588, May 2000.
- [tommasin_spitzer-irs_2010] Silvia Tommasin, Luigi Spinoglio, Matthew A. Malkan, and Giovanni Fazio. Spitzer-IRS high-resolution spectroscopy of the 12 μm seyfert galaxies. II. results for the complete data set . ApJ , 709 pp. 1257–1283, February 2010.
- [u_spectral_2012] Vivian U, D. B. Sanders, J. M. Mazzarella, A. S. Evans, J. H. Howell, J. A. Surace, L. Armus, K. Iwasawa, D.-C. Kim, C. M. Casey, T. Vavilkin, M. Dufault, K. L. Larson, J. E. Barnes, B. H. P. Chan, D. T. Frayer, S. Haan, H. Inami, C. M. Ishida, J. S. Kartaltepe, J. L. Melbourne, and A. O. Petric. Spectral energy distributions of local luminous and ultraluminous infrared galaxies . ApJS , 203 pp. 9, November 2012.
- [ulvestad_radio_1989] James S. Ulvestad and Andrew S. Wilson. Radio structures of seyfert galaxies. VII - extension of a distance-limited sample . ApJ , 343 pp. 659–671, August 1989.
- [veron-cetty_catalogue_2010] M.-P. Véron-Cetty and P. Véron. A catalogue of quasars and active nuclei: 13th edition . A&A , 518 pp. 10, July 2010.
- [wu_spitzer/irs_2009] Yanling Wu, Vassilis Charmandaris, Jiasheng Huang, Luigi Spinoglio, and Silvia Tommasin. Spitzer/IRS 5-35 μm low-resolution spectroscopy of the 12 μm seyfert sample . ApJ , 701 pp. 658–676, August 2009.
- [wynn-williams_luminous_1993] C. G. Wynn-Williams and E. E. Becklin. Luminous infrared galaxies - sizes at 10-32 microns . ApJ , 412 pp. 535–540, August 1993.
Images
Optical image (DSS, red filter). Displayed are the central 4 arcmin with North being up and East to the left. The colour scaling is linear with white corresponding to the median background (BG) and black to the 0.01% pixels with the highest intensity.
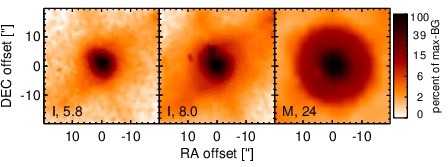
Spitzer MIR images. Displayed are the inner 40 arcsec with North being up and East to the left. The colour scaling is logarithmic with white corresponding to median BG and black to the 0.1% pixels with the highest intensity. The label in the bottom left states instrument and central wavelength of the filter in micron (I: IRAC, M: MIPS).
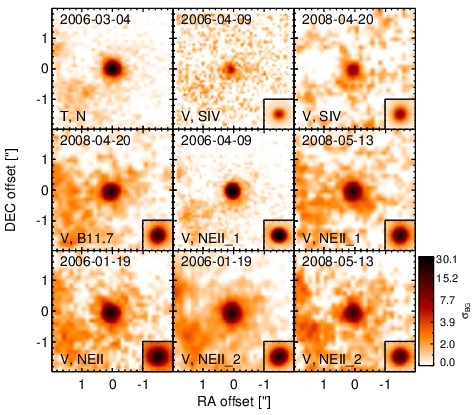
Subarcsecond-resolution MIR images sorted by increasing filter central wavelength. Displayed are the inner 4 arcsec with North being up and East to the left. The colour scaling is logarithmic with white corresponding to median BG and black to the 75% of the highest intensity of all images in units of sig_bg. The inset image (where present; either bottom or top right) shows the central arcsecond of the PSF from the calibrator star, scaled to match the science target. The labels in the bottom left state instrument and filter names (C: COMICS, M: Michelle, T: T-ReCS, V: VISIR).
SEDs
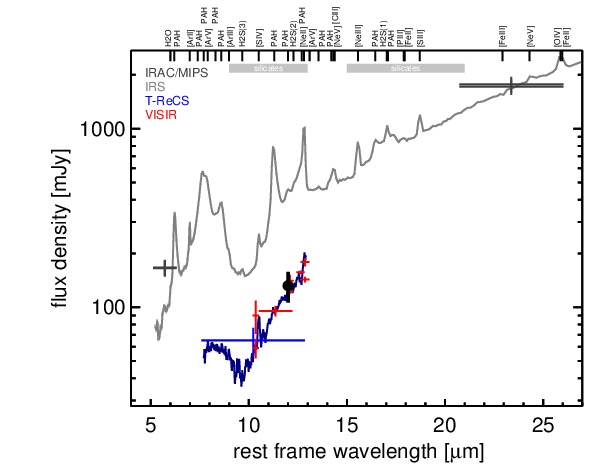
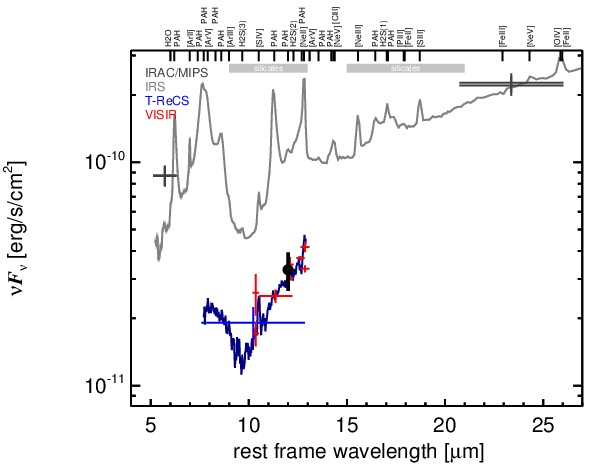
MIR SED. The description of the symbols in all the SED plots (where present) is the following: Grey crosses and solid lines mark the Spitzer/IRAC, MIPS and IRS data. The colour coding of the other symbols is as follows: green for COMICS, magenta for Michelle, blue for T-ReCS and red for VISIR data. Darker-coloured solid lines mark spectra of the corresponding instrument. The black filled circles mark the nuclear 12 and 18 micron continuum emission estimate from the data (where present). The ticks on the top axis mark positions of common MIR emission lines, while the light grey horizontal bars mark wavelength ranges affected by the silicate 10 and 18 micron features.